INDIAN CLASSICAL INSTRUMENTS
The Musical Instruments section of the Indian Culture portal contains information about a range of instruments from across India. The Indian Culture portal has researched and is happy to present information about the countless exquisite musical instruments of our country. The extent and diversity of such instruments is vast and we will keep on adding to this section.
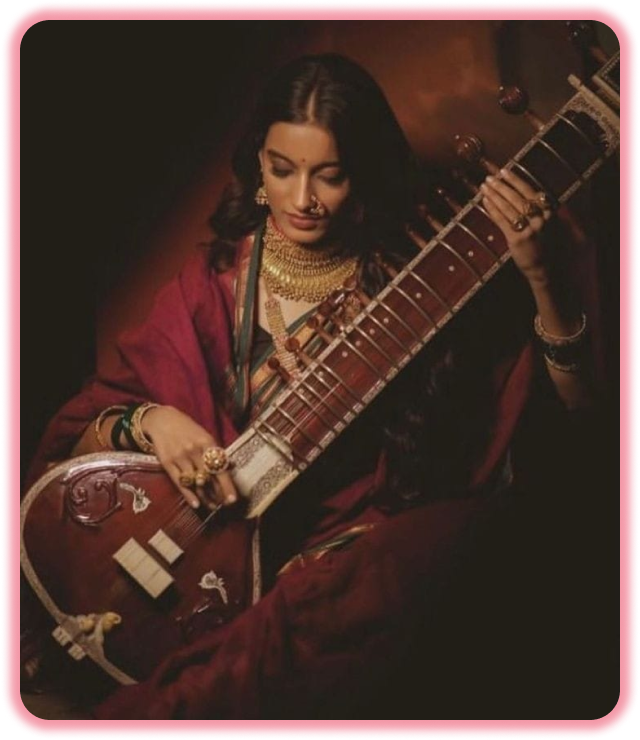

Why Sitar ?
The sitar (English: /ˈsɪtɑːr/ or /sɪˈtɑːr/; : sitāra) is a plucked stringed instrument, originating from the Indian subcontinent, used in Hindustani classical music. The instrument was invented in the 18th century, and arrived at its present form in 19th-century India. Khusrau Khan, an 18th-century figure of the Mughal Empire has been identified by modern scholarship as the inventor of the sitar. According to most historians, he developed the sitar from the setar, an Iranian instrument of Abbasid or Safavid origin.
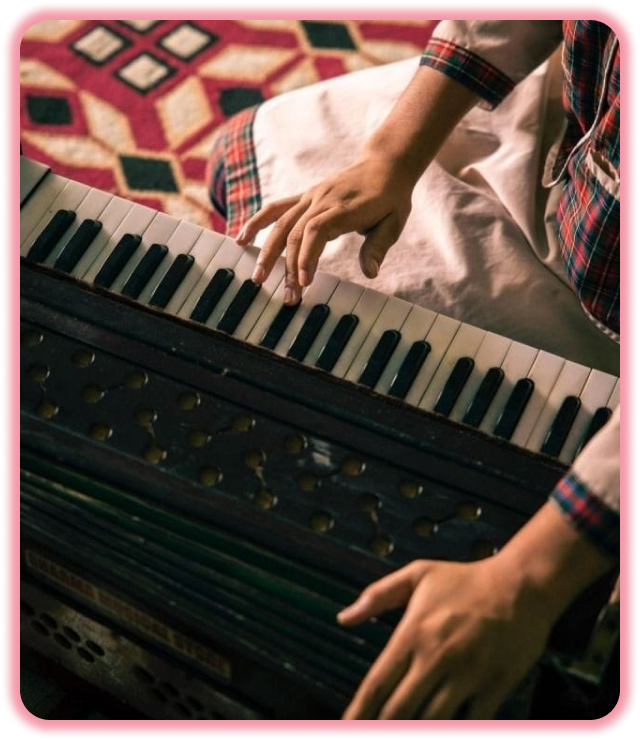


Why Harmonium ?
The harmonium repertoire includes many pieces written originally for the church organ, which may be played on a harmonium as well, because they have a small enough range and use fewer stops. For example, Bach's Fantasia in C major for organ BWV 570 is suitable for a four-octave harmonium.
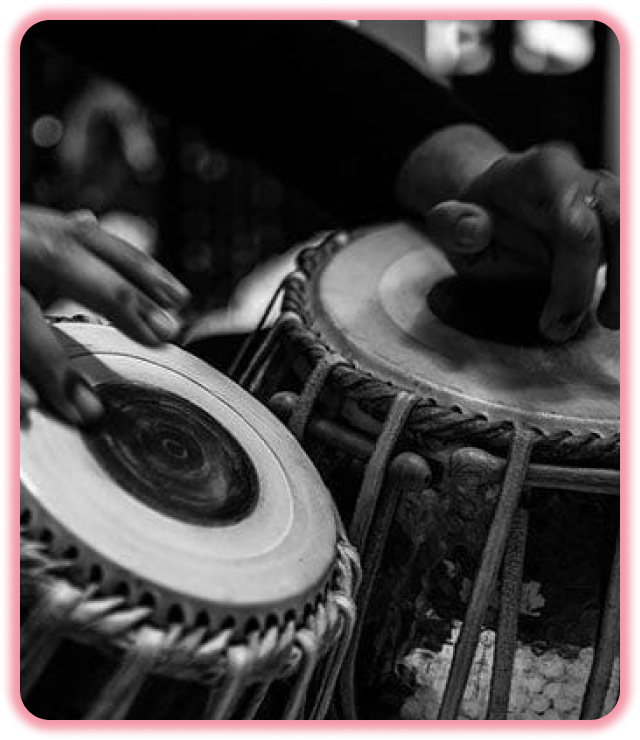


Why Tabla ?
A tabla is a pair of hand drums from the Indian subcontinent. Since the 18th century, it has been the principal percussion instrument in Hindustani classical music, where it may be played solo, as an accompaniment with other instruments and vocals, or as a part of larger ensembles. The tabla is an essential instrument in the bhakti devotional traditions of Hinduism and Sikhism, such as during bhajan and kirtan singing.
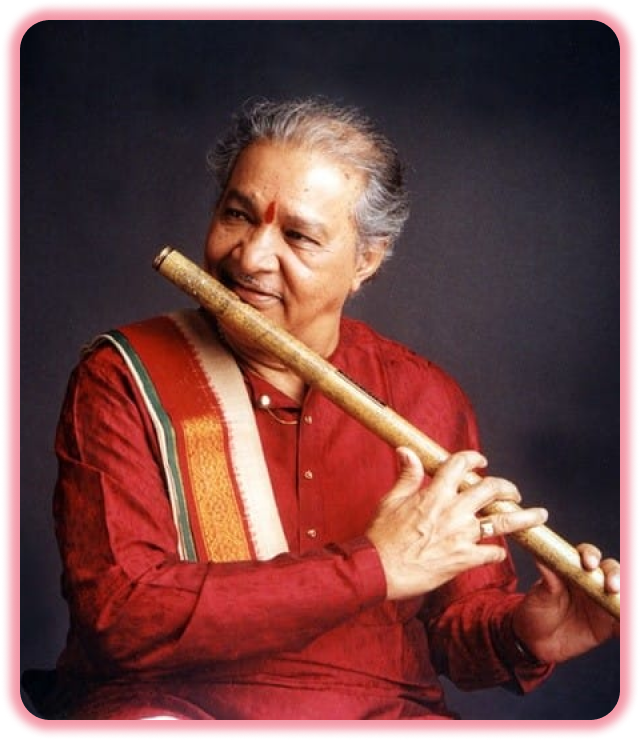


Why Flute ?
The flute is a member of a family of musical instruments in the woodwind group. Like all woodwinds, flutes are aerophones, producing sound with a vibrating column of air. Unlike woodwind instruments with reeds, a flute produces sound when the player's air flows across an opening. In the Hornbostel–Sachs classification system, flutes are edge-blown aerophones.
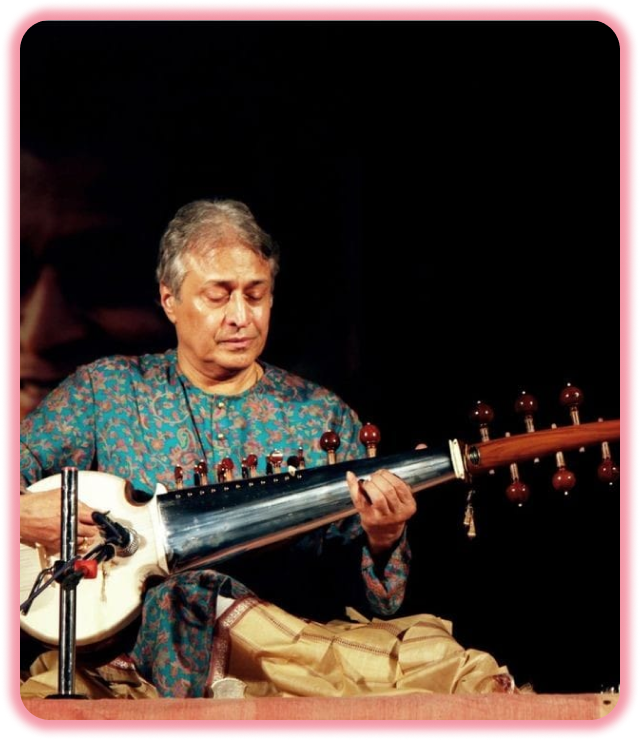


Why Sarod ?
The sarod is a stringed instrument, used in Hindustani music on the Indian subcontinent. Along with the sitar, it is among the most popular and prominent instruments. It is known for a deep, weighty, introspective sound, in contrast with the sweet, overtone-rich texture of the sitar, with sympathetic strings that give it a resonant, reverberant quality. A fretless instrument, it can produce the continuous slides between notes known as meend (glissandi), which are important in Indian music.


Why Mridangam ?
The mridangam is a percussion instrument originating from the Indian subcontinent. It is the primary rhythmic accompaniment in a Carnatic music ensemble. In Dhrupad, a modified version, the pakhawaj, is the primary percussion instrument. A related instrument is the Kendang, played in Maritime Southeast Asia. Its a complex instrument to tune and involves a lot of mathematics to construct korvais.
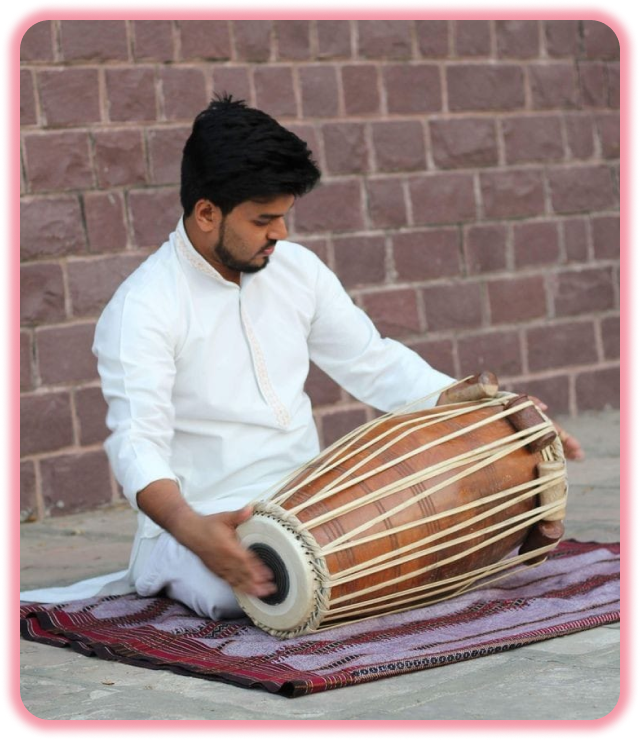


Why Pakhawaj ?
The pakhawaj is a barrel-shaped, two-headed drum, originating from the Indian subcontinent, the oldest version of double sided drums and its descendants are mridangam of Southern India and kendang of Maritime Southeast Asia and other South Asian double-headed drums. Its older forms were made with clay.
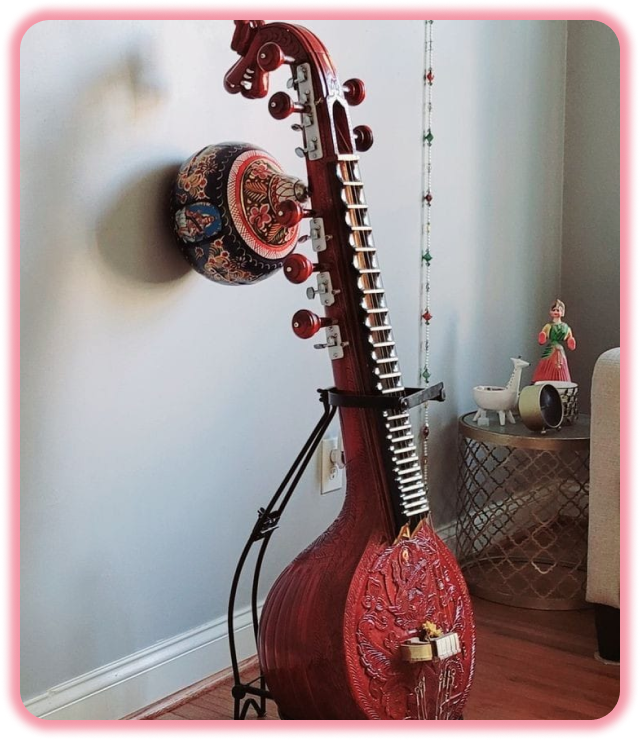


Why Veena ?
The Veena, also spelled vina (Sanskrit: वीणा : vīṇā), is any of various chordophone instruments from the Indian subcontinent. Ancient musical instruments evolved into many variations, such as lutes, zithers and arched harps. The many regional designs have different names such as the Rudra veena, the Saraswati veena, the Vichitra veena and others.
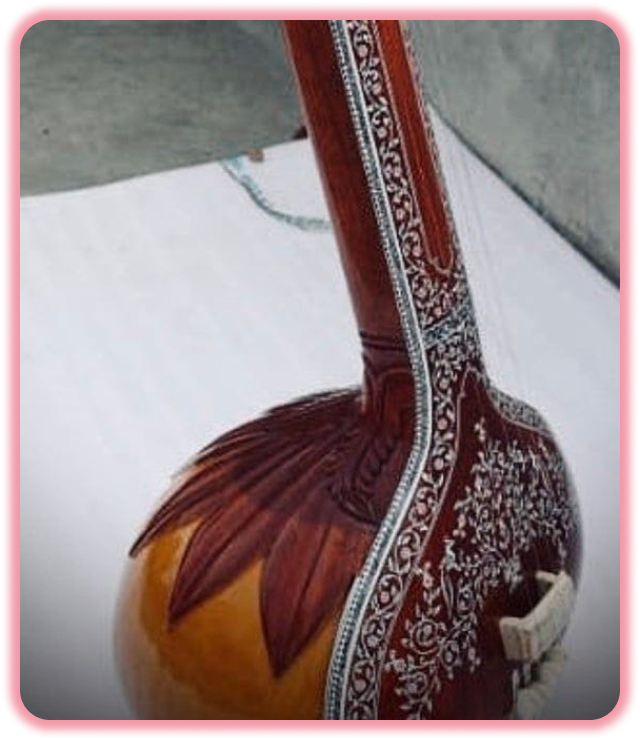


Why Tanpura ?
The Tanpura (Sanskrit: तंबूरा, romanized: Taṃbūrā) (also referred to as tambura, tanpuri, tamboura, or tanpoura) is a long-necked, plucked, four-stringed instrument originating in the Indian subcontinent, found in various forms in Indian music. Visually, the tanpura resembles a simplified sitar or similar lute-like instrument, and is likewise crafted out of a gourd or pumpkin.
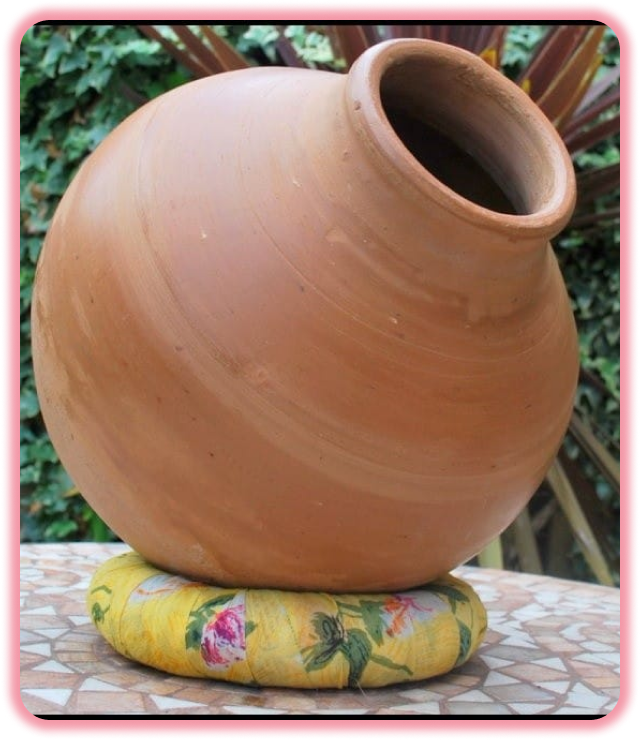


Why Ghatam ?
The ghaṭam (Sanskrit: घट, Kannada: ಘಟ ghaṭa, Tamil: கடம் ghatam, Telugu: ఘటం ghataṃ, Malayalam: ഘടം, ghataṃ) is a solid instrument used in various repertoires across the Indian subcontinent, especially in Southern India . Its variant is played in Punjab and known as gharha as it is a part of Punjabi folk traditions. Its analogue in Rajasthan is known as the madga and pani mataqa ("water jug").
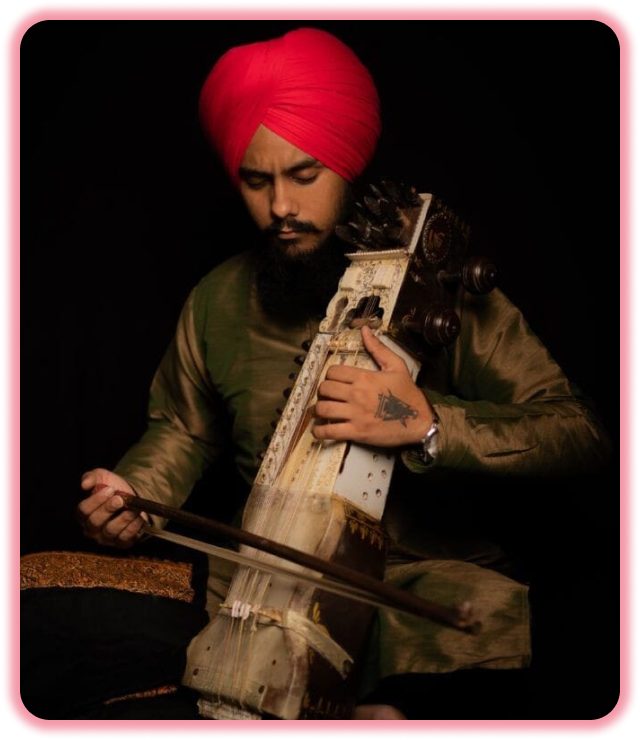


Why Sarangi ?
The sārangī is a bowed, short-necked three-stringed instrument played in traditional music from South Asia – Punjabi folk music, Rajasthani folk music, Sindhi folk music and Boro folk music (there known as the serja) – in Pakistan, South India and Bangladesh. It is said to most resemble the sound of the human voice through its ability to imitate vocal ornaments such as Gamaks or Gamakam (shakes) and meends (sliding movements). The Nepali sarangi is similar but is a folk instrument, unornate and four-stringed.
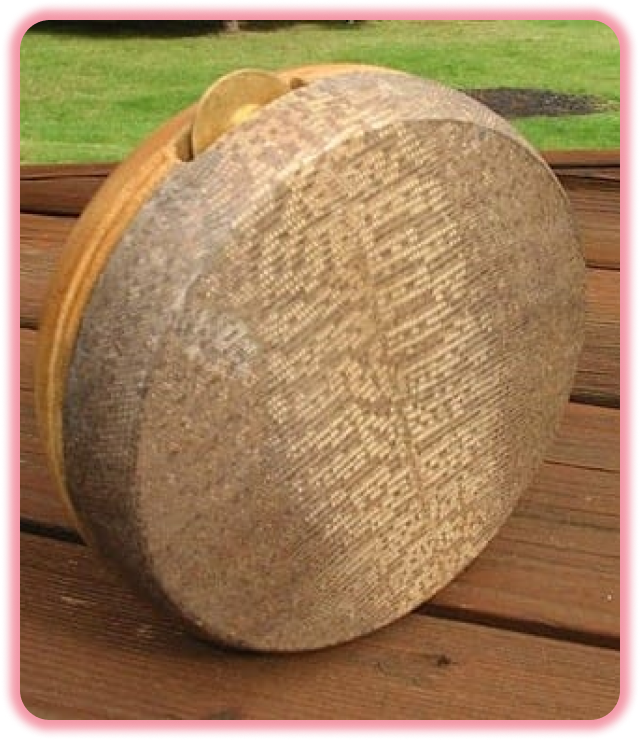


Why Kanjira ?
The kanjira, khanjira, khanjiri or ganjira, a South Indian frame drum, is an instrument of the tambourine family. As a folk and bhajan instrument, it has been used in the Indian subcontinent for many centuries. It is used primarily in concerts of Carnatic music (South Indian classical music) as a supporting instrument for the mridangam.
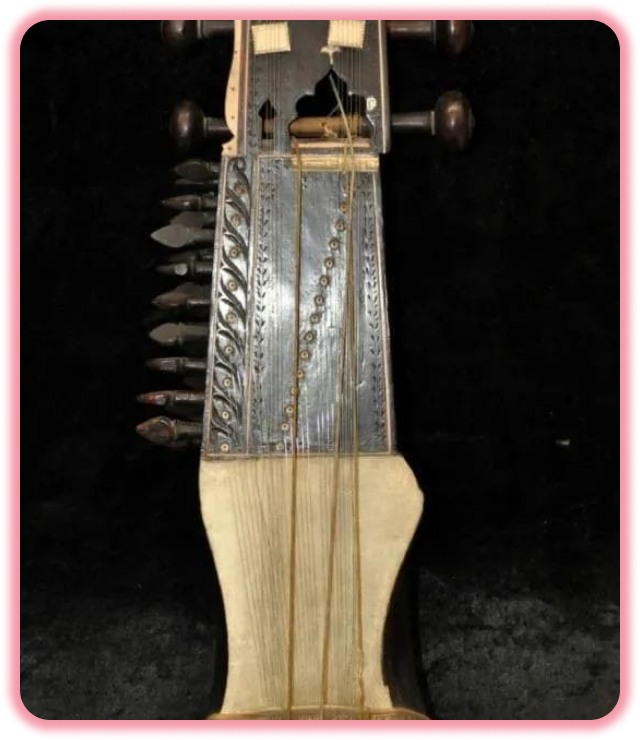


Why Dilruba ?
The Dilruba (also spelled dilrupa) is a bowed musical instrument originating in India. It is a type of Bowed Sitar that's slightly larger than an esraj and has a larger, square resonance box like a Sarangi. The dilruba holds particular importance in Sikh history. It became more widely known outside India in the 1960s through use in songs by Western artists, such as the Beatles during their psychedelic phase (most notably in the song "Within You Without You").
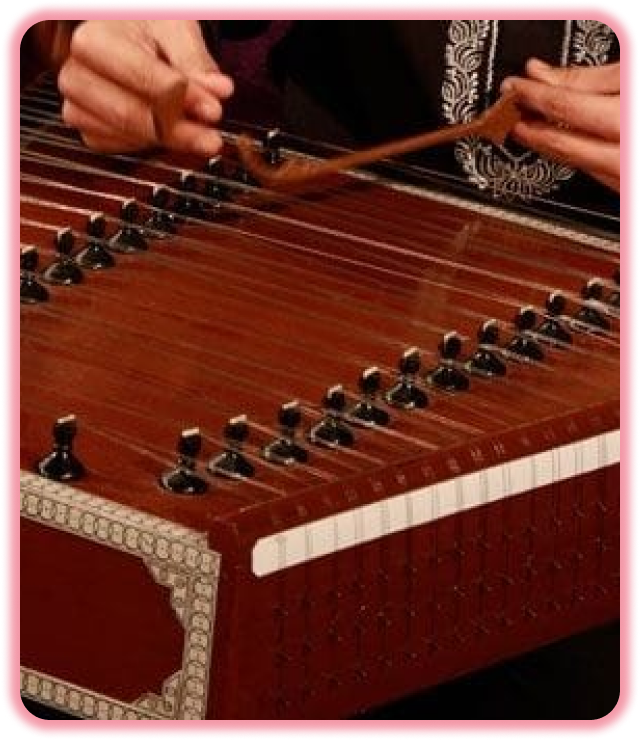


Why Santoor ?
The Indian Santoor instrument is a trapezoid-shaped hammered dulcimer, and a variation of the Iranian santur. The instrument is generally made of walnut and has 25 bridges. Each bridge has 4 strings, making for a total of 100 strings. It is a traditional instrument in Jammu and Kashmir, and dates back to ancient times. It was called Shatha Tantri Veena in ancient Sanskrit texts.
